작업 스레드 생성과 실행
2022. 4. 22. 20:36ㆍjava/java
*몇 개의 작업을 병렬로 실행할지 결정
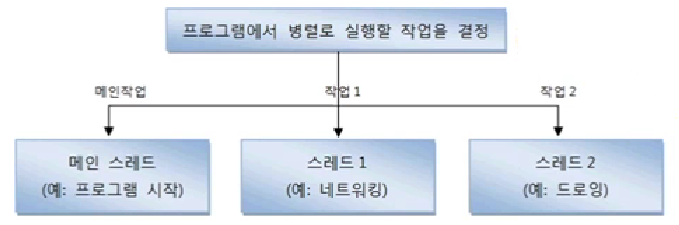
*작업 스레드 생성 방법
1) Thread 클래스로부터 직접 생성
2) Thread 하위 클래스로부터 생성
*Thread 클래스로부터 직접 생성
class Task implements Runnable {
public void run() {
스레드가 실행할 코드;
}
}
Thread로부터 run() 메소드를 실행시키는 방법
1)
Runnable Task = new Task(); //위에 만들어둔 Task클래스를 Runnable 인터페이스 데이터 타입 변수에 대입
Thread thread = new Thread(task); //Thread 객체를 만들어서 인수로 task 참조변수를 넘김
thread.start();
2)
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { //익명객체 이용
public void run() {
스레드가 실행할 코드;
}
});
thread.start();
3) 람다식
Thread thread = new Thread( () -> {
스레드가 실행할 코드;
});
thread.start();
실습)
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepPrintExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//비프음을 5번 반복해서 소리나게 하는 작업
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}싱글 스레드는 비프음을 5번 반복하고 나서야 "띵" 문자열을 5번 출력한다.
run() 메소드 실행 방법1.
//Runnable 인터페이스의 run()메서드 구현 클래스
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//비프음을 5번 반복해서 소리나게 하는 작업
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
public class BeepPrintExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable beepTask = new BeepTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(beepTask); //run()메소드를 실행시키는 방법 1.
thread.start();
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
방법2.
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepPrintExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Runnable beepTask = new BeepTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(beepTask);
thread.start();
*/
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { //익명객체 이용
@Override
public void run() {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
});
thread.start();
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
방법3. 람다식
package sec02.exam01_createthread;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepPrintExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Runnable beepTask = new BeepTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(beepTask);
*/
/*
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
});
*/
Thread thread = new Thread( () -> {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
} );
thread.start();
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}*Thread 하위 클래스로부터 생성
public class WorkerThread extends Thread { //Runnable 인터페이스를 이용하지 않고 곧바로 만듦
@Override
public void run() {
//스레드가 실행할 코드
}
}
Thread thread = new WorkerThread();
thread.start();
Thread thread = new Thread() { //익명 객체 이용
public void run() {
//스레드가 실행할 코드
}
}
thread.start
방법1
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepThread extends Thread { //직접 Thread를 상속받아 재정의
@Override
public void run() {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepPrintExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new BeepThread();
thread.start();
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
방법2.
import java.awt.Toolkit;
public class BeepPrintExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Thread thread = new BeepThread();
thread.start();
*/
Thread thread = new thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
};
//"띵" 문자열을 5번 출력하는 작업
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {Thread.sleep(500); } catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
}
*스레드의 이름
1) 메인 스레드 이름 : main
2) 작업 스레드 이름 : Thread-n
thread.getName();
3) 작업 스레드의 이름 변경
thread.setName("스레드 이름");
4) 코드를 실행하는 참조 얻기
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();